Lesson 1: Simple Present Tense
Look at the daily routine of Bina, a class VIII students of Fatikchari Girls' High
School. In pairs ask and answer questions about what Bina does at a particular
time of a typical day.
Use the following as example:
A: What does Bina do at eight o'clock in the morning?
B: She starts for school at eight o'clock.
Now, in the same pair, talk about what you do at times shown in Bina's daily
routine. Ask and answer questions about your daily activities. Use the
example below:
A: What do you do at four o'clock in the afternoon?
B: I go to the field to play football.
Look at the pictures below. What profession do these people have? In pairs
ask and answer questions about each picture. Use the example below:
A: What is his/her profession?
B: I think, he/she is a cook.
A: A cook? What does a cook do?
B: He/she cooks food in a restaurant.
What tense did you use for the activities you have done so far? Notice the
verb forms you used when talking about Bina's routine and your daily
activities. Also think about how you talked about the profession of the people
in the pictures.
While doing those activities, you actually talked about facts in general.
Now read the section below to know more about simple present tense.
Simple Present is also called Present Simple. The Simple Present expresses an
action in the present, taking place once, never or several times. It is also used
for actions that take place one after another and for actions that are set by a
timetable or schedule. The Simple Present also expresses facts in the present.
Present tense.
Can you explain the diagram? Share your ideas with a partner.
Examples:
• Windows are made of glass.
• Windows are not made of wood.
3. Scheduled Events in the Near Future
Speakers occasionally use Simple Present to talk about scheduled events in
the near future. This is most commonly done when talking about the
timetable of transportation, but it can be used with other scheduled events
too.
Examples:
• The train leaves tonight at 6 am.
•The bus does not arrive at 11 am, it arrives at 1 pm.
•When do we board the plane?
• The party starts at 8 o'clock.
Exercise 1
The following text describes the life of a fisherman. Rewrite the verbs in the
bracket to make a paragraph in the simple present tense.
A fisherman (to be) an individual whose work is to catch fish in the ponds,
canals and rivers and sell then in the local markets. His main profession (to be)
to earn his living by catching and selling fish. He even (go) to the sea in groups
to catch fish. He (have) to lead a miserable life as his daily income (to be) very
meagre. Some fishermen (live) on the seashore and (catch) fish in the sea,
while others (move) near the rivers during the rainy season. Again some
(return) to village for repairing fishing nets and boats.
A fisherman (do) not know many things happening around him. He (keep)
himself busy with fishing lines. His joy (know) no bounds when he (catch) a lot
of fish.
Exercise 2
Read the passage and answer the questions below the passage.
Mr. Amin works at a bank. He is the manager. He starts work every day at 8:00.
He finishes work every day at 6:00. He lives very close to the bank. He walks
to work every day. His brother and sister also work at the bank. But, they do
not live close to the bank. They drive cars to work. They start work at 9:00. In
the bank, Mr. Amin is the boss. He helps all the workers and tells them what
to do. He likes his job. He is also very good at his job. Many customers like Mr.
Amin and they say hello to him when they come to the bank. He likes to talk
to the customers and make them feel happy. Mr. Amin really likes his job.
Now, answer this questions:
1. What time does Mr. Amin start work?
2. Does Mr. Amin drive a car to work?
3. Does Mr. Amin talk to customers?
4. How does Mr. Amin feel about his job?
Lesson 2: Present Continuous Tense
Read the live radio commentary of a big sport event and notice the
underlined parts.
Hello listeners, welcome to the
running commentary of the annual
sport meet of Bangladesh Olympic
Association. I am speaking from the
Bangabandhu National Stadium
Dhaka. It's just eight o'clock in the
morning and we are expecting the
grand opening of the annual event
in next few minutes. As I am standing in front of the main gate, I can see the crowd enjoying this sunny morning in the Eastern gallery. Now, the President
of Bangladesh Olympic Association is entering the ground along with the
officials. The athletes are gathering in the field and they are warming up. Just
now I can see a great athlete in front of me, two times gold medalist, Jamal
Haider. He is waving his hands to the crowd and as you can hear, the
spectators are happy to see their heroes and they are cheering so loud!
Discuss the question in pairs:
How is the commentator describing the actions that are taking place while he
is talking i.e. what verb from is she/he wing here?
Now look at the people in the pictures below. In pairs ask and answer
questions about what each of them are doing at this moment. Follow the
examples below:
A: What is s/he doing?
B: S/he is ...... ing.
What tense do we use to talk about some actions that is taking place at the
time of talking? The tense we use for this is called Present Continuous tense.
This tense is also known as Present Progressive tense.
Now, read the section below to know more about Present Continuous
(progressive) tense.
The Present Progressive is a form of the verb that shows the action is going
on in the present.
The Present Progressive is used for actions going on at the moment of
speaking and for actions taking place only for a short period of time.
When do we use present continuous/progressive tense? Read the following
sentences in present continuous tense. Can you find out the different uses of
present continuous/progressive tense?
1. The boys are swimming in the pond.
2. He is studying medicine. 3. He is working very hard nowadays.
4. She is preparing a delicious curry tonight.
5. He is taking a basic computer course next month. 6. She is always making complains.
Now read the section below to know more about when or where to use this
tense.
We use Present Continuous/Progressive tense to talk about:
• Actions that are happening now (e.g. She is playing tennis.)
• Actions which are currently in progress may not be exactly at this
moment/second e.g. She is studying astrology these days.)
• Planned future actions (e.g. We are starting a new course next month.)
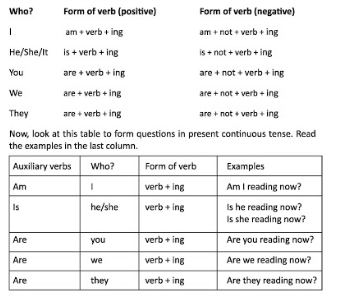
Forming sentences in present continuous tense
You have so far looked at many examples of sentences in present continuous
tense. Have you noticed how these sentences are formed? Discuss the
following questions in pairs:
1. Can you form a sentence in the Present Continuous tense without an
auxiliary verb?
2. What auxiliary verbs are used with different subjects to form these
sentences?
3. What form does the main verb take in present continuous tense?
Now, read the following part to check your understanding of how sentences
are formed in present continuous tense.
Exercise
Look at the picture. In pairs discuss the following questions about the
people in the picture.
 1. Who are they?
1. Who are they?2. Where are they sitting now?
3. What are they doing?
The text below describes the two people in this picture. Write the verbs in the
bracket in their correct forms and necessary auxiliary verbs.
Right now, it is Monday morning. Mamun and Tina are at home. They (sit)
___________at a table. They (eat).___________breakfast. At this moment, Tina
(drink)_________ coffee. She (eat).________cake. She (sit)._________________
across the table from Mamun. He is Tina's husband. He (sit).____________at
the table with Tina. He also (drink) _______ _ coffee. Mamoon (listen to)
Tina. After breakfast, Mamun and Tina (leave)_________ for
work. They work in the city. They (ride).__________the bus to work.
Lesson 3: Present Perfect Tense
Rajib and his friends have gathered in the school canteen to discuss their
preparations for a cultural show. Read the conversation between Rajib and his
friends and notice the underlined parts.
Rajib : Well, let's talk about the invitation card. When can we print them?
Mira :I have just talked to a press and the manager said he'd print them in
two days.
Rajib : That's great! Now how about donations? Have we got enough
money?
Momen : I have collected five hundred taka from bookshop.
Jalil : Our club chairman has already given two thousand.
Bonna : My sister has requested her boss to donate some money. He has
agreed to help us.
Rajib : Okay, let's hope he will give us a good amount of money. Has anyone
talked with the decorators?
Momen :I have already talked to them. They will do the stage, lighting and the
sound.
Rajib : Fantastic! Seems that all of you have done excellent jobs. Thank you.
As you read the underlined parts of the conversation, what have you noticed?
What time do these expressions refer to?
Notice that, all the underlined parts refer to actions that were completed
before the present time. Also notice that the friends are talking about actions
that have finished recently. These underlined parts are examples of
expressions in the Present Perfect tense.
When do we use Present Perfect tense? Read the following sentences in
present perfect tense. Can you guess the different uses of Present Perfect
tense?
1.He has answered the questions.
2. I have seen the film three times already.
3.He has just joined his new post.
4.I have never seen a crocodile before.
5.She has bought some food for us.
6.They have lived here for three years.
Now, read the section below to know more about when or where to use this
tense.
Present Perfect tense is used for:
•Actions that happened at an unspecific time before the present (e.g.
They have invited all of us.)
•Actions that have ended recently (e.g. She has broken her leg.)
•States that started in the past and are still continuing (e.g. I have
always liked him.)
You have so far looked at many examples of sentences in present perfect
tense.
Have you noticed how these sentences are formed? Discuss the following
questions in pairs.
1. Can you form a sentence in the Present Perfect tense without an
auxiliary verb?
2. What auxiliary verbs are used to form Present Perfect sentences?
3. What form does the main verb take in Present Perfect tense?
Now, read the following to check your understanding of how sentences are
formed in the Present Perfect tense. They are formed by using past
participle (pp) of the main verb after have/has.
They have + verb (pp) have + not + verb (pp)
Now, look at this table to form questions in the Present Perfect tense. Read
the example in the last column.
Exercise 1
Read the following story and rewrite the verbs in the brackets in correct forms
with appropriate auxiliary verbs.
Recently, it (rain) ........ in Munira's town. So far, she (see) ........ rains three
times. Munira always (love) ....... the
sound of the raindrops on her tin-shed
house. She has (be) ....... out in the rain
two times before.
Munira's daughter, Mishu never (play)
........ in the rain. This is her first
experience of playing in the rain. Munira
is worried about her daughter. She might
catch a cold.
Munira just (buy) ........ a new umbrella.
She puts on her rain coat and goes out with the umbrella.
Exercise 2
Look at the list of some everyday activities in the
box. In pairs ask and answer questions about
what you have done today. Follow the example
below:
A: Have you watched television today?
B: Yes, I have. I have watched a football match.
The Present Perfect continuous tense indicates that something began in the
past and has continued up to now or has current relevance, or is likely to
continue in future.
Lesson 4: Simple Past Tense
Read the story of Zahid, a student of class eight, who traveled to St. Martin's
island last year. Read about his journey and discuss in pairs the following
questions.
1. What problems did Zahid face during the journey?
2. How did he go to St. Martin's?
3. What things did he do at Cox's Bazar and St. Martin's island?
A Memorable Trip
I had a memorable trip to Cox's Bazar and St. Martin's Island when I was astudent of class seven. I remember all the things happened to me during
the trip. My uncle and aunt lived in Chittagong at that time and they
invited us to visit them. My cousin Saleha was of the same age as I was. So
I felt delighted when my mother told me about the visit. We live in
Rajshahi and Chittagong is far away. First we planed to go to Dhaka by bus
and then to Chittagong by train. One fine morning we got on a bus at
Rajshahi at 7 o'clock in the morning. Normally it takes about six hours to
reach Dhaka from Rajshahi. Unfortunately, there was a huge traffic jam
from on the way and the journey took almost eight hours to reach Dhaka.
So we had to stay in a hotel in Dhaka for the night and the next morning we
took the train to Chittagong at 8 in the morning from Kamlapur railway
station. We were unlucky again because the train also arrived late at
Chittagong. But we felt happy because my uncle and aunt received us at
the station.
Next morning we started for Cox's, Bazar. We arrived there at about two
and spent the rest of the day by the sea side. I had not seen the sea earlier
so it was an exciting experience for me. We stayed at a hotel there. Early
next morning we went to the beach again and saw the beautiful sunrise.
We walked along the beach, bathed in sea water, ate sea food and enjoyed
ourselves.
Read the text again and look at the words that express actions in the past.
You will find that these actions words are all verbs. You will also find the be
verbs (was and were) used in the sentences for describing a situation in the
past.
The sentences that describe a past situation or action in the above text are in
Simple Past tense.
Can you say when or where we use Simple Past tense? The Simple Past
expresses an action in the past taking place once, never, several times.
Read the text below on Gautam Buddha and think about the uses of Simple
Past tense.
Buddha was born in the year 563 B.C. at a place called Lumbini. His father
Suddhodana was a Sakya king and his mother Maya also came from a princely
family. Seven days after his birth his mother died, leaving him to the care of
her sister and his step mother Mahajapati.
The young Buddha was brought up in Kapilavastha, the capital of Sakya
kingdom. When he was born, several miracles occurred. His father and some
prominent members of his court were aware that a divine child was born
amidst them. His parents gave him the name Siddhartha. They expected him
to grow and become a successful and king.
Read the section below to know about the uses of Simple Past tense.
Simple Past tense is used to express -
• action in the past taking place once, never or several times
Example: He visited his parents every weekend.
• actions in the past taking place one after another
Example: He came in, took off his coat and sat down.
• action in the past taking place in the middle of another action
Example: When I was having breakfast, the phone suddenly rang.
Forming sentences in Simple Past tense
Discuss the questions in pairs:
1. How do you form sentences in simple past tense?
2. Do all simple past tense sentences have auxiliary verbs?
3. What form does the main verb take in simple past tense?
4. How do you form a question about the past?
Exercise 1
In pairs talk about a journey you made. One partner will ask the following
questions and the other will answer them in simple past tense.
1. Where did you go?
2. What transport did you take?
3. When did you start?
4. How long was the journey?
5. Did you take any luggage with you?
6. Did you face any troubles on the way?
7. When did you reach your destination?
Exercise 2
Put the verbs into the correct tense (Simple Past or Present Perfect). Note that
we do not use the present perfect when past time is mentioned.
A: 1(see / not) ----------------- you for a long time. Where ----------------- (you
/ be)?
B: 1(come / just) ------------------ back from Cox's Bazar.
A: Oh really? What (you / do) ------------------ there?
B: 1 (stay) ------------------ at a hotel and (enjoy) -------- the beauty of the
sea.
Read what the students were doing at 7'o clock in the morning. What tense
are they using in their reply? They are talking about what was happening in
the past.
Read the text below. Underline the sentences in Simple Past tense and Past
Continuous tense.
Yesterday, it was raining all
day. Onu was playing inside
the house. She wanted to be
outside. She wasn't playing
outside because it was
raining. She was feeling tired
of staying inside the house.
Onu was trying to keep busy
inside the house. She was
reading her book until the
electricity went out. Then, she decided to practise her sewing. She was
practising sewing until lunchtime. After lunch, she sat by the window and
watched the rain.
While Onu was watching the rain, the phone rang. Her mother was calling to
say she was coming home. She played the games with her mother when she
came home.
Discuss the questions in pairs.
a) Why was Onu feeling tired?
b) What were Onu doing to get herself busy?
c) What did Onu do with her mother?
d) How are the sentences formed in the past continuous?
Read about the uses of Past Simple and Past Continuous tense.
When we talk about two actions in the past taking place one after another, we
use simple past tense for both the actions.
Example: She came home and switched on the computer and checked
her mails.
But when we talk about two events in the past which were taking place at the
same time, we use Past Continuous for describing both the actions.
Example: Sumon was playing on the computer while his brother was
watching.
Non-progressive verbs
The following verbs are usually only used in Simple Past (not in the
progressive form).
state: be, cost, fit, mean, suit
Example: We were on holiday.
possession: belong, have
Example: Salam had a pet.
senses: feel, hear, see, smell, taste, touch
Example: He felt the cold.
feelings: hate, hope, like, love, prefer, regret, want, wish
Example: Joynal loved cakes.
perceptions: believe, know, think, understand
Example: I did not understand him.
introductory: clauses for direct speech: answer, ask, reply, say
Example: “I am watching TV," he said.
Exercise
Put the verbs into the correct tense (Simple Past or Past Progressive).
1. The receptionist (welcome)the guests and (ask)
------------them to fill in the form.
2. The car (break) ---------------down and we (have)-------------to walk home.
3. My father (come).-------------in, (look) -------------around and
(tell)-------------me to tidy up my room.
4. While the parents (have)------------------breakfast, their children (run)
------------about.
5. Momota (turn).-----------------off the lights and (go).-----------------to bed.
Lesson 6: Simple Future Tense
Mr. Kabir is going to Singapore tomorrow. Here is his planning for the
journey. Work in pairs, ask and answer the following questions.
The flight will leave Dhaka
Sahjalal International Airport at
11.00 pm and I must report for
checking-in at least two hours
before the departure time. I
shall start for the airport by 7-00
pm so that I can reach the
airport in time. There will be
heavy traffic on the Airport Road
at this time. If I start by 7.00 pm,
I'll have enough time in hand to
reach the airport. I am going to
take only a small suitcase and a laptop with me. So, there won't be any hassle
with my baggage. I have not got any foreign currency but I am going to buy
some dollars from the airport. This will be a short flight and I hope to arrive at
the Chengi Airport, Singapore in 3 hours.
Questions
a) What time will the flight leave Shahjalal International Airport?
b) What things is Mr. Kabir taking with him?
c) What tense is used by Mr. Kabir to talk about the travel?
In the passage above Mr. Kabir talks about the events/actions that will happen
in future. So he uses Simple Future tense to talk about the things that will take
place in future.
Read the following sentences. Can you see a common structure in them? In
pairs, try to identity the structure.
•The flight will leave Dhaka Sahjalal International Airport at 1.00 pm.
•I shall start for the airport by 7-00 pm.
•There will be heavy traffic on the Airport Road.
•This will be a short flight.
•There won't be any hassle with my baggage.
Now, read the following section to check your understanding of Simple Future
tense.
To make sentences in the Simple Future tense, we put'will or ...Il' before the
base form of the verb.
For the negative we put 'will not' or 'won't' in front of the verb. With subjects
like 'l' or 'we', we can also say 'shall/shan't.
To make questions in the future, we put 'will' or 'shall in front of the subject.
With 'and 'We' you can use shall. This usually means a suggestion or that
something is not certain.
What will you be in future? Tell your friends in your class. (hints: teacher,
doctor, pilot, nurse, etc.)
Read the sentences below and notice how we talk about future plans.
I am going to buy some dollars from the airport.
I am going to take only a small suitcase and a laptop with me
She is going to sit for the exam next year.
Now, read the text below and notice the future expressions with going to +
verb.
On Saturday, Noboni will be three year old. Her parents are going to have a
birthday party. The party is going to begin at noon on Saturday. Many people
will be invited at the party. Noboni will have so much fun!
Noboni's mother is going to cook polaow and chicken curry. Her father is going
to buy a special cake. It will be a chocolate cake. Noboni will love her cake! Her
grandmother is going to bring some ice cream and her aunt is going to buy her
a nice dress.
Exercise 1
Kona met a fortune teller once. Though she does not believe in fortune telling,
she wanted to have some fun and so, asked the fortune teller to tell about her
future. The fortune teller was also very funny. Here is what the fortune teller
told her. Complete the sentences with appropriate auxiliary verbs.
1. You (earn).______________a lot of money.
2. You (travel)______________around the world.
3. You (meet)_______________lots of interesting people.
4. Everybody (admire)_________________you.
5. You (not / have) _______________________any problems.
6. Many people (serve)________________________.you
7. They (anticipate)___________________your wishes.
8. There (not/be)___________________anything left to wish for.
9. Everything (be)_________________perfect.
10. But all these things (happen / only)._________if you marry me.
Exercise 2
Ms. Selina Rahman is talking about her holiday. Complete the sentences. Put
the verbs in brackets into the Simple Future tense.
1. I........ ............... my holidays with my parents this year. (spend)
2. We ........................ at my parents' house in Khulna. (stay)
3. My father .. .................... ..... at the station to receive me. (be)
4. I .................................some warm clothes. (need)
5. I.. .. ............... some presents for my parents. (take)
6. It................... a great time with my parents. (be)
Exercise 3
Talk about your future plans in pairs. Say at least three things that you are
going to do next week. Use the 'going to' form.




















Post a Comment